Chronic diseases pose the greatest health risk and contribute greatly to death and disability rates in the US, as well as drive up annual health care costs. 6 in 10 adults[1] in the US live with at least one chronic disease, while 4 in 10 adults have two or more comorbid conditions. Ranking high on the list of top chronic diseases is Diabetes Mellitus (DM), which brings along with it a host of potential complications. Hence, an effective diabetes mellitus care is an important priority for good health outcomes.
The Importance of Blood Sugar Control in Diabetes Mellitus Care
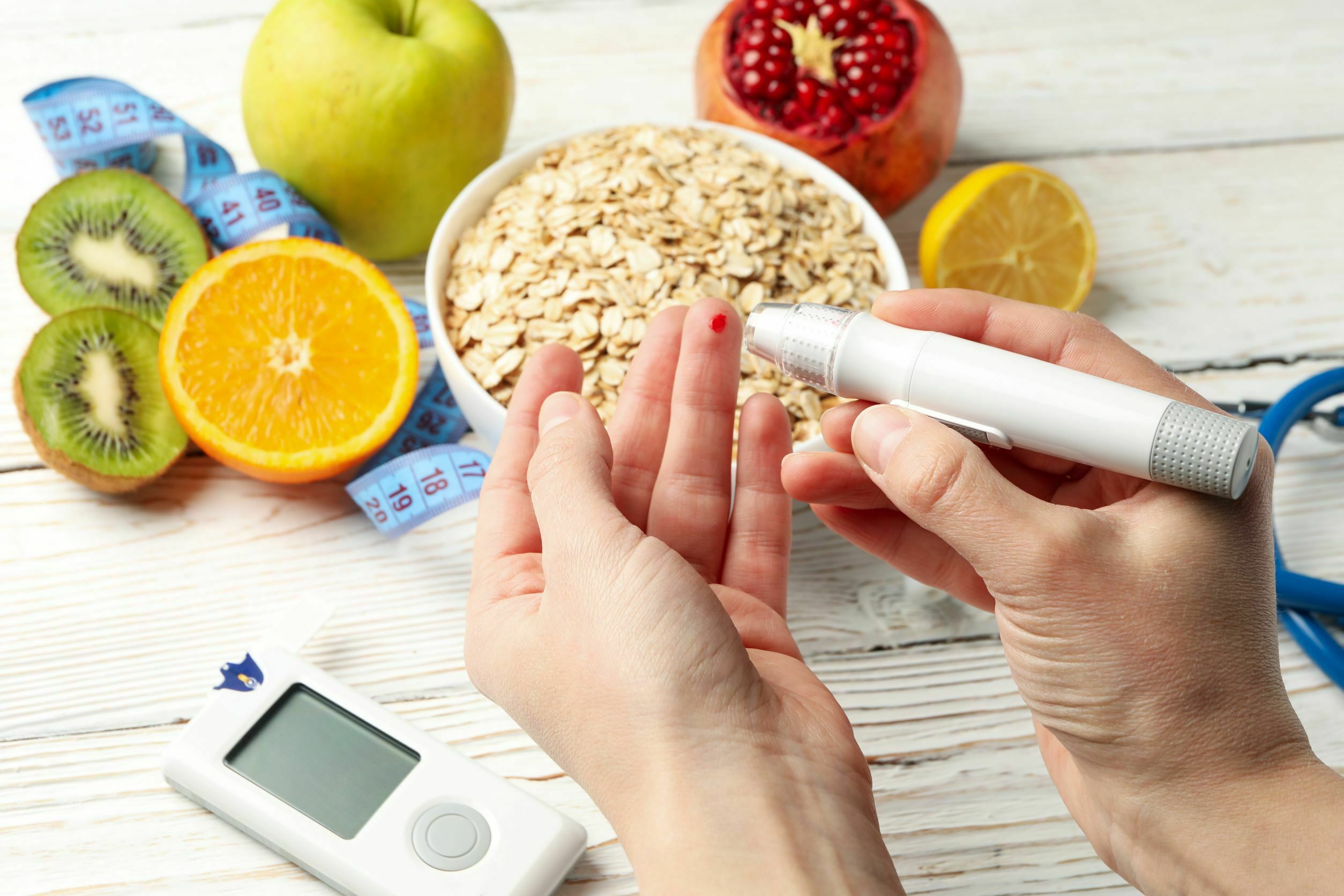
Good blood sugar control[2] is the cornerstone to effective Diabetes Mellitus care management and helps prevent or delay long-term complications associated with it such as heart, kidney, or eye disease. Diet and lifestyle interventions, coupled with medications and regular blood sugar monitoring, are the most common strategies recommended to reach target blood sugar levels. Timely and appropriate changes to these strategies usually require close follow-up with patients’ providers, which unfortunately may not always be feasible during this time of the pandemic. Hence, remote patient monitoring (RPM) and telehealth solutions, such as DrKumo’s platform and system of connected devices, helps bridge the gap between patients and providers.
Remote Monitoring and Health Outcomes on Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Despite RPM being a fairly recent trend in healthcare, there are a plethora of articles examining its usefulness in managing Diabetes. One study[3] published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research found that information technology-based interventions were associated with a significant reduction in HbA1c levels (mean difference -0.33%), with electronic self-management systems demonstrating the largest HbA1c reduction (0.50%). In another study[4] published in the BMC Health Services Research, pooled evidence from four systematic reviews found that utilizing telehealth remote monitoring interventions led to a small but significant improvement in HbA1c levels (-0.55%) compared with usual care.
Given the fact that most oral medications for DM have an average expected HbA1c lowering of 0.5%, this improvement in HbA1c levels from telehealth interventions may translate to one less pill the patient needs to take. In the long run, this HbA1c reduction may lead to less chances of developing chronic complications related to DM.
DrKumo Remote Patient Monitoring Solution
DrKumo provides a wide array of RPM tools that are useful in managing DM. Included in this system are wireless medical devices such as weighing scales, glucometers, continuous glucose monitoring devices, and blood pressure monitors, which can collect important patient-related parameters that providers can view in real-time. This information in turn can aid providers in making appropriate and timely recommendations to patients regarding their treatment regimens, which can lead to better health outcomes and help reduce unplanned clinic or emergency room visits.
Takeaway
Remote patient monitoring definitely makes a difference for people living with DM, helping them monitor important health-related parameters, reach their target HbA1c levels, and enable better communication with their health providers. This will lead to better health outcomes, less chances of long-term complications, and fewer unplanned hospital visits.
To know more about how you can use RPM for Diabetes Care Management, click this RPM Comprehensive Guide.
References:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022, January 24). Chronic diseases in America. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/chronicdisease/resources/infographic/chronic-diseases.htm
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021, April 28). Manage blood sugar. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/managing/manage-blood-sugar.html
- Alharbi, N. S., Alsubki, N., Jones, S., Khunti, K., Munro, N., & de Lusignan, S. (2016, November 25). Impact of information technology-based interventions for type 2 diabetes mellitus on glycemic control: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of medical Internet research. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5148808/
- Lee, P. A., Greenfield, G., & Pappas, Y. (2018, June 26). The impact of telehealth remote patient monitoring on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of systematic reviews of randomised controlled trials. BMC health services research. Retrieved https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6019730/