Remote patient monitoring (RPM) for diabetes management has become increasingly popular as it provides clinicians with valuable information about a patient’s daily glucose levels without being physically present.
This guide will provide you with tips on how to implement RPM for your patients, as well as key considerations to keep in mind. First, let’s take a look at what RPM is and what it can offer your patients.
What is Remote Patient Monitoring?
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) is a technology-based healthcare delivery method that allows medical professionals to monitor patients outside of traditional in-person visits. This is typically done by using a combination of wireless devices and telecommunication technologies to transmit patient physiologic data, such as vital signs and medical information, to healthcare providers in real-time. With the help of remote monitoring, healthcare providers can track patients’ health status and make adjustments to their treatment plans as necessary, without the patient needing to visit the clinic or hospital in-person.
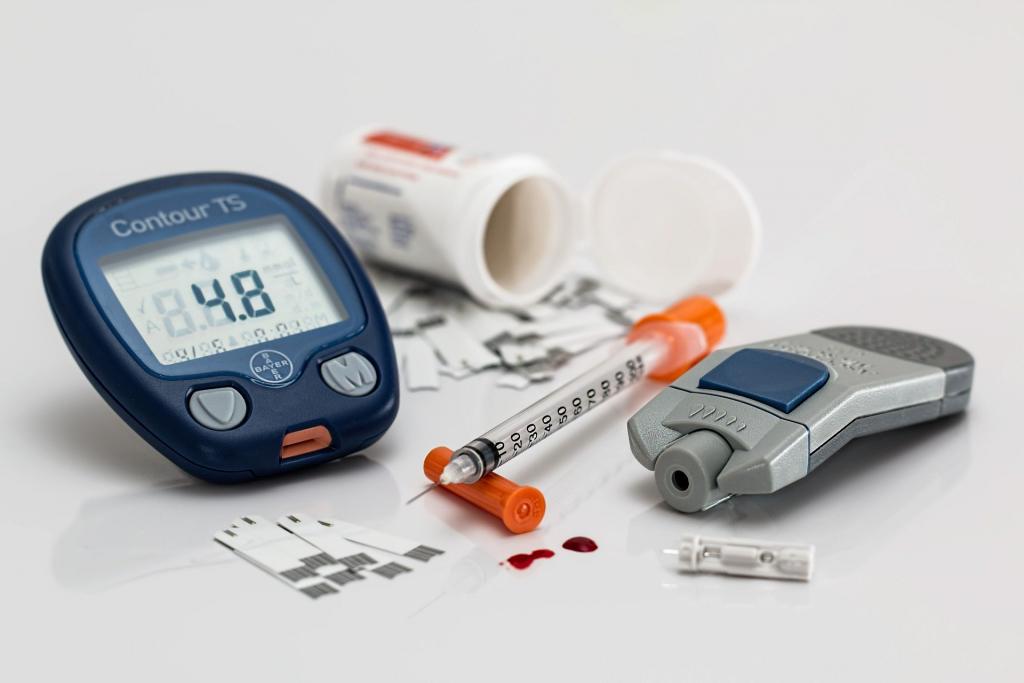
RPM can be used for a variety of conditions, including chronic illnesses such as diabetes, heart disease, and lung disease. In the case of diabetes, for example, RPM can include the use of continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) or glucometers to transmit glucose levels to healthcare providers in real-time. This allows healthcare providers to monitor patients’ blood sugar levels and adjust their insulin doses or medication regimens as necessary, reducing the risk of complications such as hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
RPM can also include the use of other monitoring devices such as blood pressure monitors, weight scales, and pulse oximeters. These devices can transmit information to healthcare providers, who can then use the data to monitor patients’ vital signs and assess their overall health.
The Challenges of Diabetes Management
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder that affects millions of people worldwide, but it is a well-known fact that Type 2 Diabetes can be managed through a combination of lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, and medication. One of the primary goals of diabetes management is to keep blood sugar levels within a normal range; otherwise, patients with high sugar levels can have a variety of complications, such as heart disease, nerve damage, kidney disease, and amputations.
On the other hand, low blood sugar levels, or hypoglycemia, can also be dangerous, causing seizures or unconsciousness in severe cases. Therefore, physicians prescribe effective glucose management to prevent these complications and maintain patient’s overall health and quality of life. While the factors involved in diabetes and its management are well-understood in the medical community, the effective management of diabetes is still challenging with many patients. This is where RPM comes in.
Remote Patient Monitoring for Diabetes Management
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) is a technology-based healthcare delivery method that allows medical professionals to monitor patients outside of traditional in-person visits. In the context of diabetes management, this typically involves the use of wireless devices and telecommunication technologies to transmit patient data, such as glucose levels, to healthcare providers in real-time, as many times as desired or prescribed by the patient’s provider. This allows healthcare providers to more effectively monitor patients’ blood sugar levels – because they have far more measurements to examine – and adjust their treatment plans as necessary, without the patient needing to visit the clinic or hospital in-person.
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) are devices that are worn by diabetes patients and measure glucose levels in the interstitial fluid, the fluid between the cells, through a small sensor inserted under the skin. The device sends glucose data wirelessly to a receiver, which displays the glucose levels, and also sends them to a cloud-based platform that can be accessed by the patients and their care providers. Glucometers, on the other hand, are devices that use a small amount of blood, obtained by pricking the patient’s finger, to measure the glucose level.
Regular and frequent patient participation in RPM programs is crucial for their effectiveness. When patients regularly and frequently monitor their glucose levels and share the information with their healthcare providers, the providers can make adjustments to the patient’s treatment plans as necessary, and catch potential issues early on, reducing the risk of complications.
Additionally, by involving patients in the monitoring process, it can encourage them to take a more active role in their own care, leading to improved patient outcomes. This is one of the reasons why it is important for patients to be educated and trained on how to use monitoring devices to facilitate the frequent participation in the program.
Implementing an RPM Program for Diabetes Management
Steps for Implementing an RPM Program for Diabetes Management in a Healthcare Setting
Implementing an RPM program for diabetes management in a healthcare setting involves several steps, including:
- Identifying the patients who would most benefit from the program, such as those with poorly controlled diabetes or those who live in remote or underserved areas.
- Assessing the patient’s needs and selecting appropriate monitoring devices, such as CGMs or glucometers.
- Educating patients on how to use the monitoring devices and how to transmit the data to healthcare providers.
- Setting up a system for transmitting and storing patient data, such as cloud-based platforms.
- Establishing a protocol for healthcare providers to access and analyze patient data, and then make treatment adjustments as needed.
- Regular follow up with the patients, such as via telehealth technology, to monitor patients’ progress, and provide support and education as necessary.
- Reviewing the program’s effectiveness by measuring the patient’s glucose control, HbA1c, and other metric of interest
The Role of Healthcare Providers in Setting Up and Managing the Program
Healthcare providers play a key role in setting up and managing an RPM program for diabetes management. They are responsible for identifying patients who would benefit from the program, selecting appropriate monitoring devices, and educating patients on how to use them.
They also need to set up a system for transmitting and storing patient data and establish protocols for accessing and analyzing the data. Additionally, healthcare providers are responsible for regularly monitoring patients’ progress and making treatment adjustments as necessary.
Tips for Effectively Communicating the Program to Patients and Educating Them on How to Use the Monitoring Equipment
The following are helpful tips healthcare providers can use when communicating with their patients on the proper use of RPM:
- Using simple, easy-to-understand language when communicating the program and its benefits to patients.
- Providing patients with written materials, such as brochures and instructional guides, to reference as needed.
- Showing patients how to use the monitoring devices in person and providing hands-on training.
- Offering ongoing support and education, such as virtual check-ins or follow-up phone calls, to ensure that patients understand how to use the devices and are comfortable with the program.
- Encouraging patients to ask questions and express any concerns they may have.
Measuring the Effectiveness of RPM for Diabetes Management
Discussion of the various metrics used to measure the effectiveness of RPM for diabetes management
There are several metrics that can be used to measure the effectiveness of RPM for diabetes management. Some of the most commonly used metrics include:
- HbA1c levels: HbA1c is a measure of average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months. Lower HbA1c levels indicate better glucose control and are associated with a lower risk of diabetes-related complications.
- Glucose readings: Monitoring blood glucose levels on a frequent basis and checking for the overall trend, including spikes and drops in glucose level, and also how it reacts to medication and food intake.
- Medication adherence: Monitoring if the patient is taking their medication as prescribed, and also how it affects their glucose level.
- Quality of life: Monitoring the patient’s overall quality of life, and how the RPM program affects it.
- Patient satisfaction: Monitoring the patient’s satisfaction with the program and their perceived improvements in their diabetes management.
Discussion of studies and research on the effectiveness of RPM for diabetes management
Several studies have been conducted on the effectiveness of RPM for diabetes management, with many showing very promising results. A meta-analysis of multiple studies found that patients who used RPM in conjunction with traditional diabetes management methods had significantly lower HbA1c levels than those who did not. Additionally, studies have also shown that RPM can lead to improved glucose control, increased patient satisfaction, and improved quality of life.
DrKumo’s Remote Patient Monitoring Solution for Diabetes Care
DrKumo offers a comprehensive selection of RPM tools specifically designed for diabetes management. These tools include wireless medical devices such as weight scales, glucose meters, continuous glucose monitoring devices and blood pressure monitors, which can collect vital patient data that can be viewed in real-time by healthcare providers.
By having access to this information, providers can make informed and prompt recommendations to patients regarding their treatment plans, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes and fewer unplanned clinic or emergency department visits.
Takeaways
Diabetes is a serious disease that can lead to a variety of complications, some of which can be life-threatening. By instituting RPM for diabetes management, providers can help their patients achieve better blood sugar control and reduce their risk of developing diabetes-related complications.
By using DrKumo’s remote patient monitoring solutions, you can ensure that your patients have easy access to the information they need to manage their diabetes effectively.
Want to start using remote patient monitoring for diabetes? Contact DrKumo now.