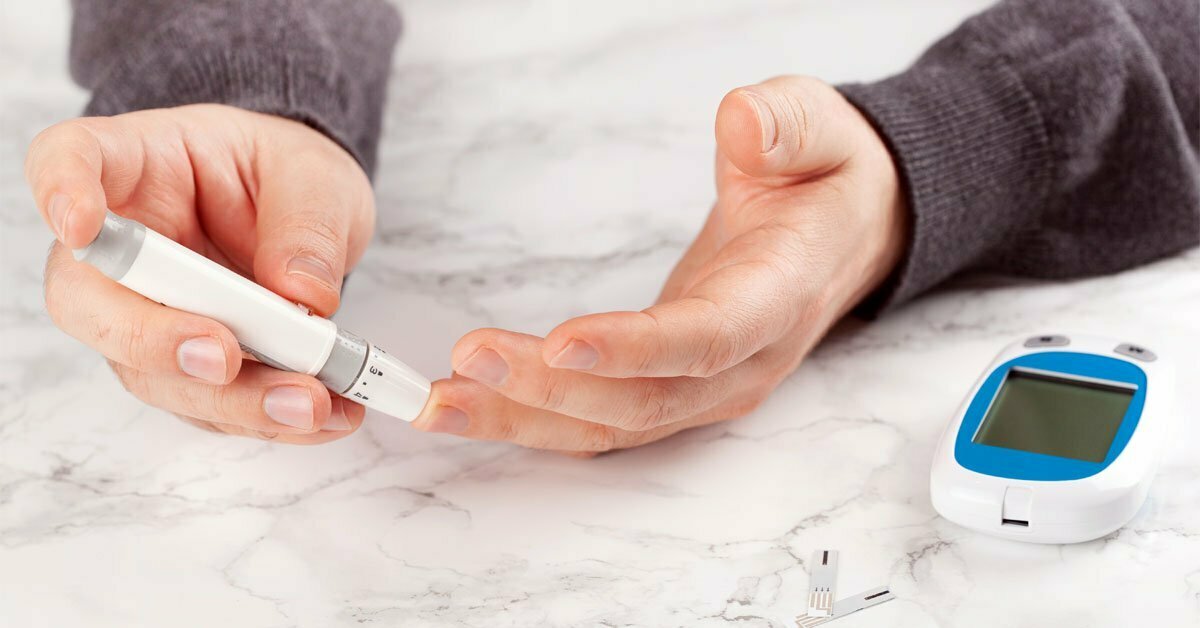
Diabetes foot care is vital as your journey does not have to include amputation. You can lower your chance of significant consequences by doing everything you can to control your blood sugar and take care of your feet. Here’s how to stay standing on your own two feet if you have diabetes and how remote patient monitoring can help you in this journey.
Diabetic Foot Risk Determination
In order to effectively manage diabetes foot care, risk identification is critical. People with diabetes for more than 10 years, who are male, have poor glucose control, or have cardiovascular, retinal, or renal issues are more likely to develop ulcers or amputations. The following foot-related risk factors have been linked to a higher risk of amputation:
- loss of protective feeling in peripheral neuropathy,
- evidence of heightened stress (erythema, hemorrhage under a callus),
- bony malformation,
- decreased or absent pedal pulses,
- ulcers or amputations in the past.
Constant monitoring of sugar and trend determination provided by remote patient monitoring provides useful information for risk determination.
Foot Nerve Damage Prevention
Remote patient monitoring can help prevent nerve damage by promoting blood sugar control. Poor blood glucose control can lead to nerve injury in the foot. Numbness, coldness in the legs, tingling, pins and needles sensation in the feet, and scorching sensations in the legs and feet are common symptoms, which are most obvious in bed at night. One of the most important predictors of ulceration and amputation is distal symmetric polyneuropathy. Because you can’t feel any pain, these symptoms can create a lack of sensitivity in your feet, which increases the chance of accidental harm. A foot injury can lead to an ulcer on the bottom of the foot that can penetrate to the bone. This could result in a bone infection as well as a persistent infection in the bones and joints. If an infection isn’t treated as soon as it appears, it might lead to ulceration and finally amputation.
Blood Supply Promotion
Remote patient monitoring provides information of your daily sugar control and can prevent deviations in the normal sugar measurements. Poor blood glucose management can cause a lack of blood supply to the feet. This renders persons with diabetes more susceptible to infection after any skin injury. The signs of a weak blood supply include leg cramps after walking short distances or climbing stairs, pain in the foot often in the early hours of the morning, feet that is reddish-blue in color, and wound-cuts that take a long time to heal.
High-Risk Conditions Prevention
High risk and low risk are the two forms of foot risk. Knowing the risks and caring for your feet might help you avoid serious issues like ulceration and amputation. Maintaining glucose levels as close to normal as feasible might considerably postpone the onset of a high-risk condition. People with one or more high-risk foot conditions should have their feet checked more frequently for the development of new risk factors and other comorbidities. Blood pressure control, weight control and sugar control all play an important role in prevention of high-risk condition in diabetics, especially amputation. Blood pressure, weight and sugar monitoring via remote patient monitoring promote more adequate self-care.
Healthy Lifestyle Promotion
Real time monitoring provided by remote patient monitoring can make you aware of the current levels of blood sugar, making you more conscious of your sugar control. Experts advise limiting your intake of sugar and simple carbs and eating meals with a low glycemic index. Low-glycemic foods are those that are less likely to trigger a blood sugar surge. It has been proven that eating meals with a low glycemic index lowers blood sugar levels. Aside from diet, regular exercise and increasing your activity also helps improve this condition.
Takeaway
Diabetes patients are more likely to develop foot ulcers due to microvascular, neuropathic, and biomechanical abnormalities in the foot. Remote patient monitoring can help patients in diabetes foot care and avoid potential amputation by providing ways to monitor blood sugar levels.